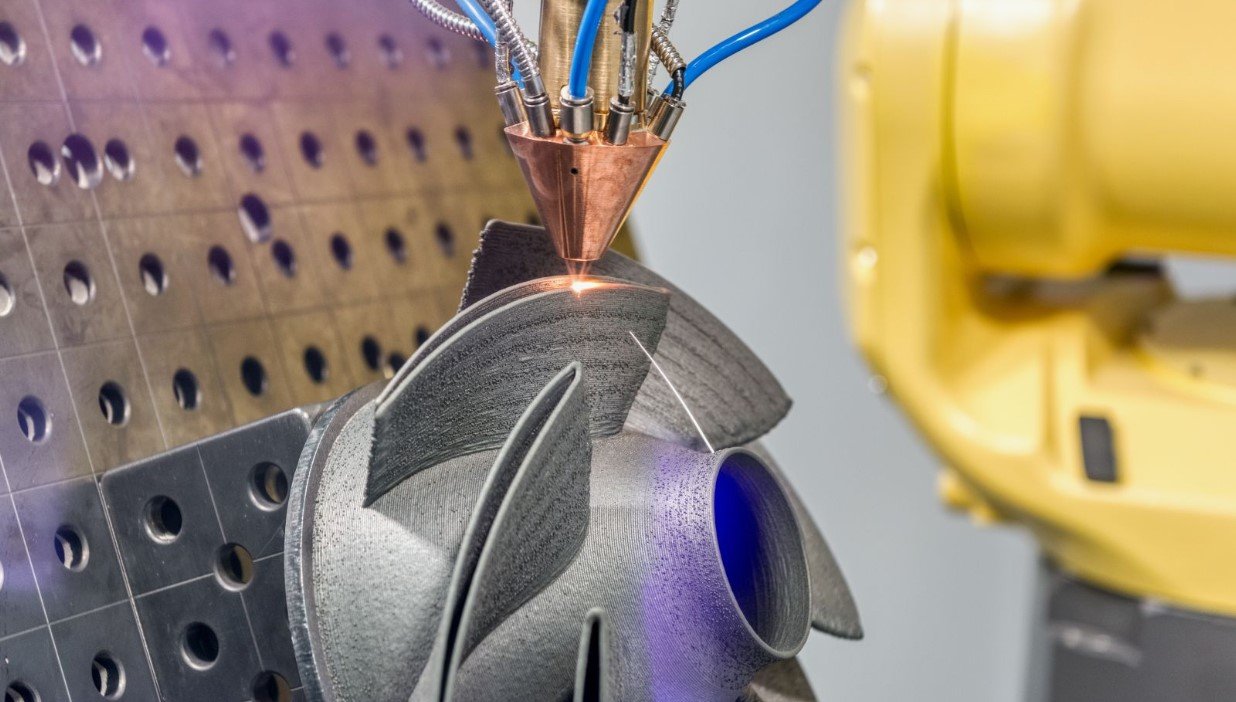
3D metal printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has transformed the way industries design, prototype, and manufacture complex components. This cutting-edge technology allows for the creation of highly intricate metal parts with exceptional precision, durability, and efficiency. In this article, we delve into the world of 3D metal printing, exploring its advantages, applications, and impact on various industries.
What is 3D Metal Printing?
3D metal printing is an innovative manufacturing process where metal objects are built layer by layer using a digital design file. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods, which involve cutting or machining material away from a block, 3D metal printing adds material layer by layer to create the final product. This allows for unparalleled design freedom and minimal material waste.
The most commonly used methods in 3D metal printing include:
- Selective Laser Melting (SLM): Uses a high-powered laser to melt and fuse metallic powders.
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): Similar to SLM but focuses on sintering metal powders instead of fully melting them.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Utilizes an electron beam for fusing metal powder in a vacuum environment.
Advantages of 3D Metal Printing
1. Design Freedom and Complexity
One of the most significant benefits of 3D metal printing is the ability to create complex geometries that are impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. From intricate lattice structures to internal cooling channels, designers can push the boundaries of innovation without limitations.
2. Reduced Material Waste
Unlike conventional machining, which often generates excess scrap, 3D metal printing is a highly material-efficient process. By adding material layer by layer, only the required amount of metal is used, resulting in cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint.
3. Customization and Rapid Prototyping
3D metal printing enables the rapid production of customized parts tailored to specific applications. This is particularly valuable in industries such as aerospace and healthcare, where bespoke solutions are critical. Additionally, it drastically reduces prototyping time, allowing for faster iterations and shorter development cycles.
4. Lightweight yet Strong Components
By incorporating lattice structures or hollow designs, 3D metal printing can produce lightweight components without compromising strength. This makes it an ideal choice for industries that prioritize weight reduction, such as automotive and aerospace.
5. Shorter Supply Chains
With 3D metal printing, manufacturers can produce parts on demand, reducing the need for extensive inventories and long supply chains. This leads to lower logistics costs and faster delivery times.
Applications of 3D Metal Printing
1. Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace industry has embraced 3D metal printing for its ability to produce lightweight, high-performance components. From turbine blades to rocket engine parts, additive manufacturing allows for the creation of complex structures that enhance fuel efficiency and reduce overall weight.
2. Healthcare and Medical Devices
In healthcare, 3D metal printing is used to produce custom implants, surgical instruments, and prosthetics. Titanium implants, for example, can be tailored to fit a patient’s anatomy perfectly, improving outcomes and patient comfort.
3. Automotive Industry
Automotive manufacturers leverage 3D metal printing to create lightweight yet durable parts, such as engine components and heat exchangers. It also facilitates rapid prototyping, enabling quicker development of new vehicle designs.
4. Industrial Manufacturing
3D metal printing is revolutionizing traditional industrial manufacturing by enabling the production of tooling, molds, and spare parts with exceptional precision. Its ability to create on-demand parts also reduces downtime and maintenance costs.
5. Jewelry and Art
Artists and jewelers use 3D metal printing to craft intricate designs that were previously unachievable with conventional methods. This technology opens new possibilities for creativity and innovation in the art world.
Challenges in 3D Metal Printing
While 3D metal printing offers remarkable benefits, it also comes with its challenges:
- High Initial Costs: The upfront investment for 3D metal printing equipment and materials can be significant.
- Material Limitations: Not all metals are suitable for 3D printing, and the availability of specialized powders may be limited.
- Post-Processing Requirements: Printed parts often require additional post-processing, such as heat treatment or surface finishing, to achieve the desired properties.
The Future of 3D Metal Printing
As technology advances, 3D metal printing is expected to become even more accessible and versatile. Innovations in metal powders, printing speeds, and machine capabilities will continue to drive adoption across industries. Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning will enhance the optimization of designs and manufacturing processes.
Industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and energy are likely to witness unprecedented growth in 3D metal printing applications, further solidifying its position as a game-changing technology.
Conclusion
3D metal printing is revolutionizing the way we manufacture and design products. From its ability to create complex geometries to its environmental benefits, this technology is shaping the future of industries worldwide. As adoption grows and advancements continue, 3D metal printing will undoubtedly remain at the forefront of modern manufacturing.